Input cell
One Ring to rule them all...
An input cell is a multi tool. By the default it assumes Wolfram Language as an input, however, it can be altered by the directive in the first line. See Markdown, Javascript, WLX, HTML, Slides, and so on.
For example
Think about it if it was an anonymous file
Then whatever you typed, you should press Shift-Enter to make magic happen.
When you start typing, the following happens
- each character is send to a server and updates the cell (autosaving every 300 ms)
- editor tries to figure out the language or a cell type
- considering (2) it changes the syntax highlighting, autocomplete / other plugins

Cell properties
By clicking on ... (more icon) located on the right side of a cell group, you can change the properties of an input cell
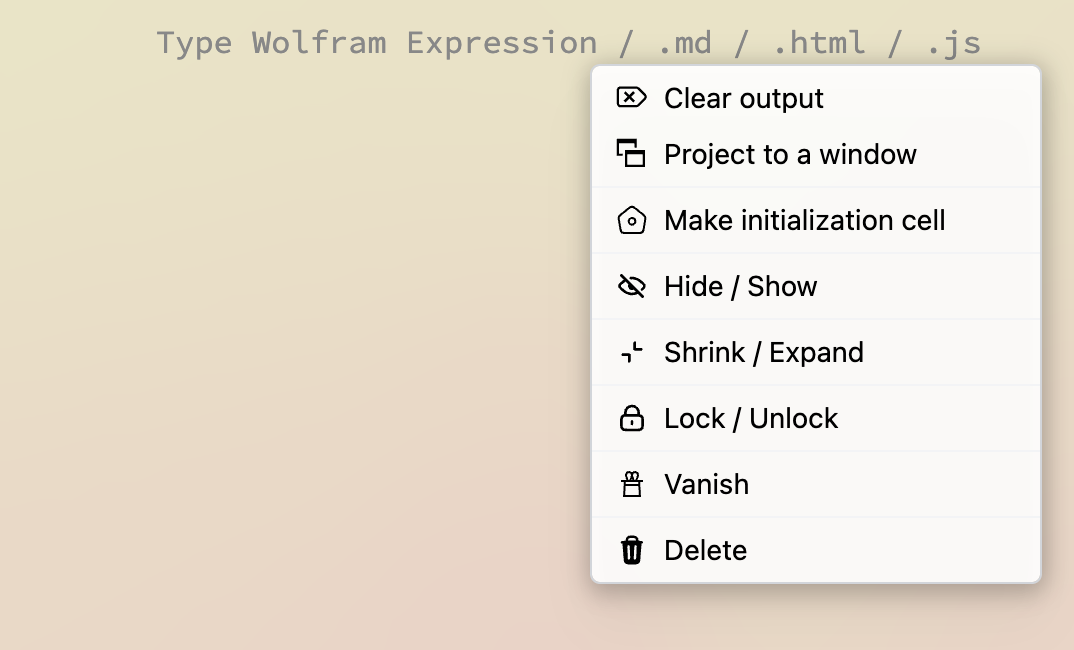
It affects the whole cell group, i.e. input cell & all children output cells. The following transformations are possible
- Project to a window - evaluates a cell and shows the first output result in a separate window
- Make initialization cell - marks an input cell as initialization cell, which will be evaluated once a notebook has been opened (appears as a green dot in the top-right corner)
- Hide / Show - hides an input cell keeping only its output cells. There is a shortcut
Cmd+2 / Alt+2or an arrow symbol on the left side of the group. - Shrink / Expand - fades out the large text keeping only the preview of it. A cursor can still be navigated into it.
- Lock / Unlock - makes an input read-only and limits the controls of the given input cell
- Vanish - makes a cell group completely invisible and uneditable. If an output cell has JS or HTML code, it will anyway be executed, however not visible explicitly. Invisible cells can only be viewed using
Expert Mode(located in the settings menu). It comes useful for making templates.
Wolfram Language
Syntax highlighting symbols tracking
Wolfram Language autocomplete and highlighting can be extended using external packages.
Once you have defined something in Wolfram Kernel session in Global` context, the corresponding symbol appears in the autocomplete window and is shared between all opened notebooks.
On the startup Wolfram Kernel reads all packages imported and fetches ::usage directives for defined symbols.
Syntax sugar
All equations typed in the editor are compatible with any WL kernels, i.e. can be used in wolframscript, since the syntax sugar and the structure is localized inside comments
For example
becomes
(*SqB[*)Sqrt[2\[Pi]](*]SqB*)
which is safe for copying to anywhere outside the WLJS ecosystem.
You do not need a mouse to construct and edit complex equations.
Unlike Wolfram Mathematica our StandardForm output is always compatible with InputForm.
The following shortcuts are often used for equations typing
-
Ctrl-2- place a square root on the selected text -
Ctrl-/- make a fraction -
Ctrl--- make a subscript -
Ctrl-6- make a superscript (power) -
ESC+..- to enter greek characters -
Alt+/Cmd+/- to comment a line -
Hold
Altto create multiple carets -
Cmd/Ctrl+F- search in the current cell
As well as the standard layout
-
ArrowLeft:
cursorCharLeft(selectCharLeftwith Shift) -
ArrowRight:
cursorCharRight(selectCharRightwith Shift) -
Ctrl-ArrowLeft (Alt-ArrowLeft on macOS):
cursorGroupLeft(selectGroupLeftwith Shift) -
Ctrl-ArrowRight (Alt-ArrowRight on macOS):
cursorGroupRight(selectGroupRightwith Shift) -
Cmd-ArrowLeft (on macOS):
cursorLineStart(selectLineStartwith Shift) -
Cmd-ArrowRight (on macOS):
cursorLineEnd(selectLineEndwith Shift) -
ArrowUp:
cursorLineUp(selectLineUpwith Shift) -
ArrowDown:
cursorLineDown(selectLineDownwith Shift) -
Cmd-ArrowUp (on macOS):
cursorDocStart(selectDocStartwith Shift) -
Cmd-ArrowDown (on macOS):
cursorDocEnd(selectDocEndwith Shift) -
Ctrl-ArrowUp (on macOS):
cursorPageUp(selectPageUpwith Shift) -
Ctrl-ArrowDown (on macOS):
cursorPageDown(selectPageDownwith Shift) -
PageUp:
cursorPageUp(selectPageUpwith Shift) -
PageDown:
cursorPageDown(selectPageDownwith Shift) -
Home:
cursorLineBoundaryBackward(selectLineBoundaryBackwardwith Shift) -
End:
cursorLineBoundaryForward(selectLineBoundaryForwardwith Shift) -
Ctrl-Home (Cmd-Home on macOS):
cursorDocStart(selectDocStartwith Shift) -
Ctrl-End (Cmd-End on macOS):
cursorDocEnd(selectDocEndwith Shift) -
Enter:
insertNewlineAndIndent -
Ctrl-a (Cmd-a on macOS):
selectAll -
Backspace:
deleteCharBackward -
Delete:
deleteCharForward -
Ctrl-Backspace (Alt-Backspace on macOS):
deleteGroupBackward -
Ctrl-Delete (Alt-Delete on macOS):
deleteGroupForward -
Cmd-Backspace (macOS):
deleteToLineStart -
Cmd-Delete (macOS):
deleteToLineEnd -
Alt-ArrowLeft (Ctrl-ArrowLeft on macOS):
cursorSyntaxLeft(selectSyntaxLeftwith Shift) -
Alt-ArrowRight (Ctrl-ArrowRight on macOS):
cursorSyntaxRight(selectSyntaxRightwith Shift) -
Alt-ArrowUp:
moveLineUp -
Alt-ArrowDown:
moveLineDown -
Shift-Alt-ArrowUp:
copyLineUp -
Shift-Alt-ArrowDown:
copyLineDown -
Escape:
simplifySelection -
Ctrl-Enter (Cmd-Enter on macOS):
insertBlankLine -
Alt-l (Ctrl-l on macOS):
selectLine -
Ctrl-i (Cmd-i on macOS):
selectParentSyntax -
Ctrl-[ (Cmd-[ on macOS):
indentLess -
Ctrl-] (Cmd-] on macOS):
indentMore -
Ctrl-Alt-\\ (Cmd-Alt-\ on macOS):
indentSelection -
Shift-Ctrl-k (Shift-Cmd-k on macOS):
deleteLine -
Shift-Ctrl-\\ (Shift-Cmd-\ on macOS):
cursorMatchingBracket -
Shift-Alt-a:
toggleBlockComment
The following EMACsy style key-bindings are also available on MacOS
Ctrl-b:cursorCharLeftCtrl-f:cursorCharRightCtrl-p:cursorLineUpCtrl-n:cursorLineDownCtrl-a:cursorLineStartCtrl-e:cursorLineEndCtrl-d:deleteCharForwardCtrl-h:deleteCharBackwardCtrl-k:deleteToLineEndCtrl-Alt-h:deleteGroupBackwardCtrl-o:splitLineCtrl-t:transposeCharsCtrl-v:cursorPageDown
For integrals, derivatives and series use Command palette tool for entering special characters.
DateObject, Graphics and many things you probably got used in Mathematica are implemented. Please see the overview in Symbolic programming
If an output is too big, it will be truncated or converted into a temporal symbol (if possible) to reduce the load on the editor
You can also make your own custom representation of your symbol like in Mathematica using MakeBoxes. Please see InterpretationBox, Interpretation and MakeBoxes and ArrangeSummaryBox, ViewBox, BoxBox and an ultimate guide on them in Decorating symbols
Access to documentation
Click on 🔎 icon in autocomplete window to open docs on that symbol in a new window

Morph output cell into input
If you change something in the output Wolfram Language cell, it will be automatically converted into a new input cell.
Auto-upload files
Drag and drop a file to the editor and paste a media from a clipboard. By the way you can always have an access to clipboard using ReadClipboard
Other languages
Most of other languages used as input do support
- auto-upload files or importing media from a clipboard
- autocomplete
- highlighting and code parsing (more than just tokenizing)