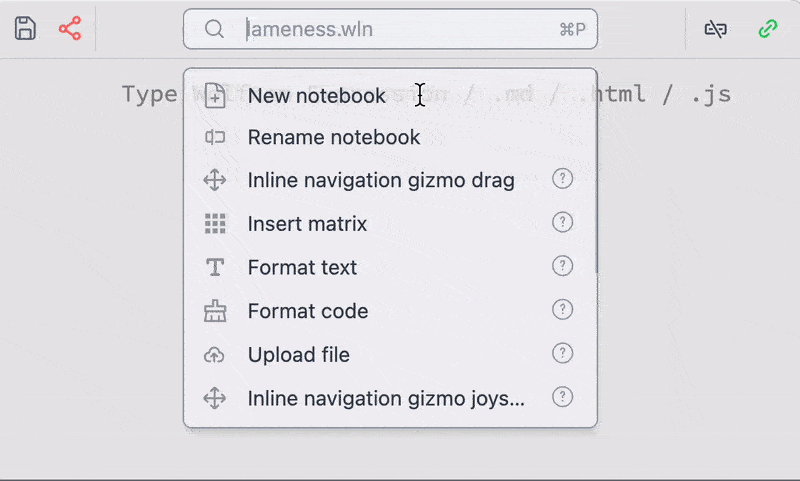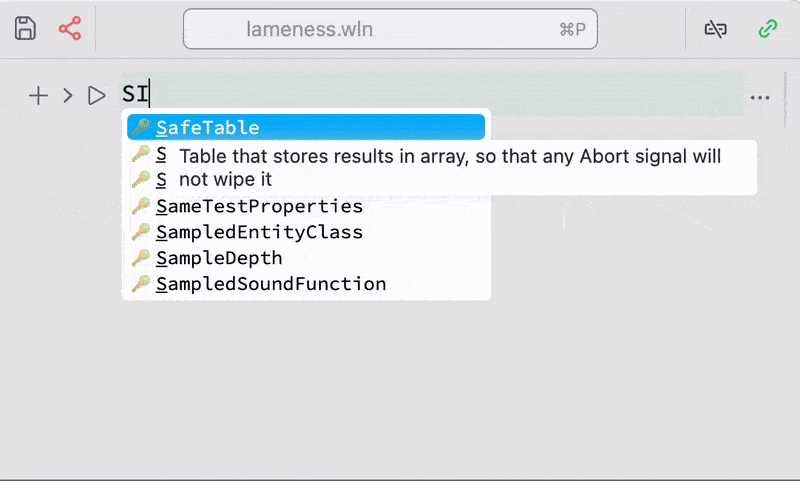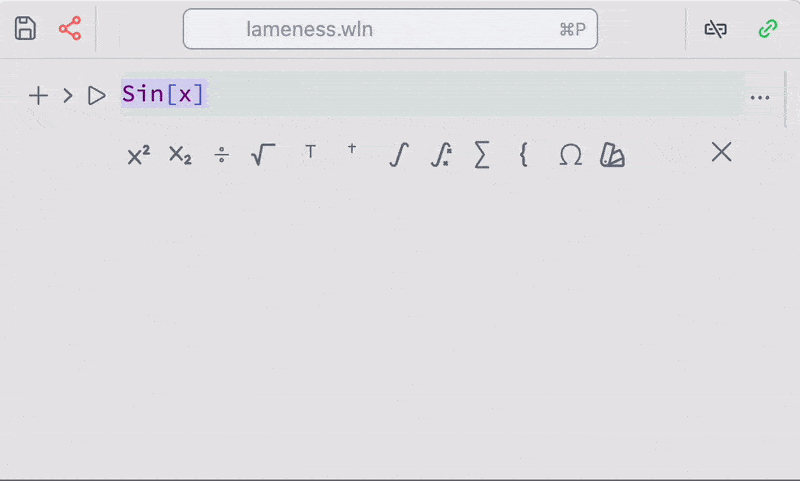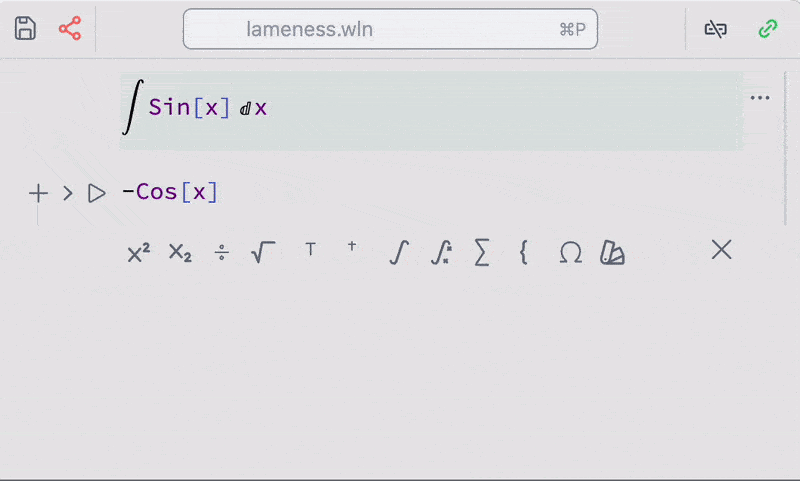
Command palette
The big power of customization comes with a powerful command palette system. This is provided by a plugin shipped with a core package.
Command palette item are mostly special cells of Wolfram / WLX / Javascript which serve a single utility function saved in a normal notebook. They are available from the command palette and have an access to your notebook and computational Kernel. You can see their source notebook as well as short documentation by clicking on a question mark symbol
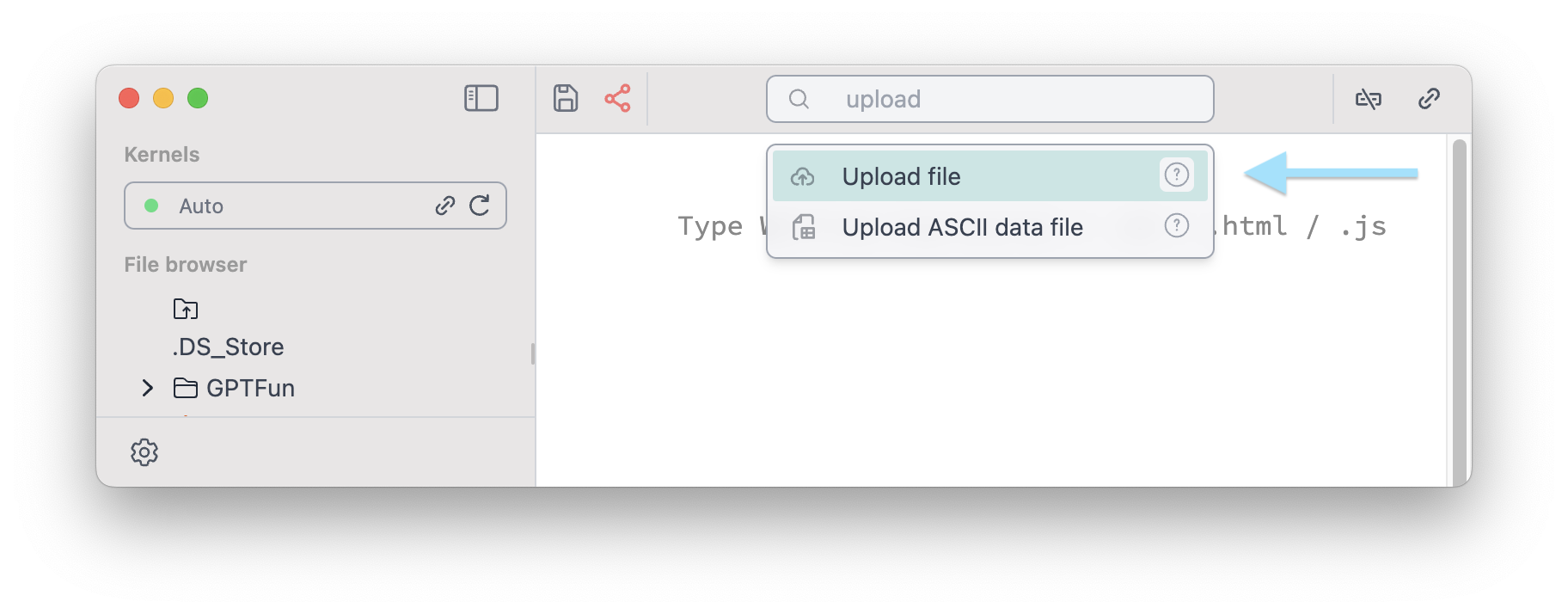
Use a shortcut for command palette Cmd + P or Ctrl + P
Context menu
If you need to apply Simplify or highlight selected expressions in the code
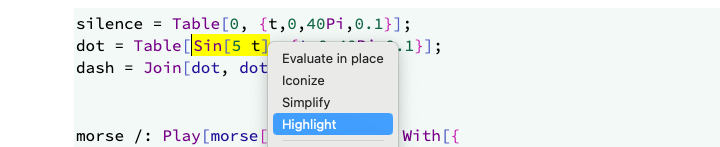
Highlighting text is not destructive and will not alter an initial expression you had.
Notebook Templates
The is a relatively new feature, that allows to create a new notebook based on a given template
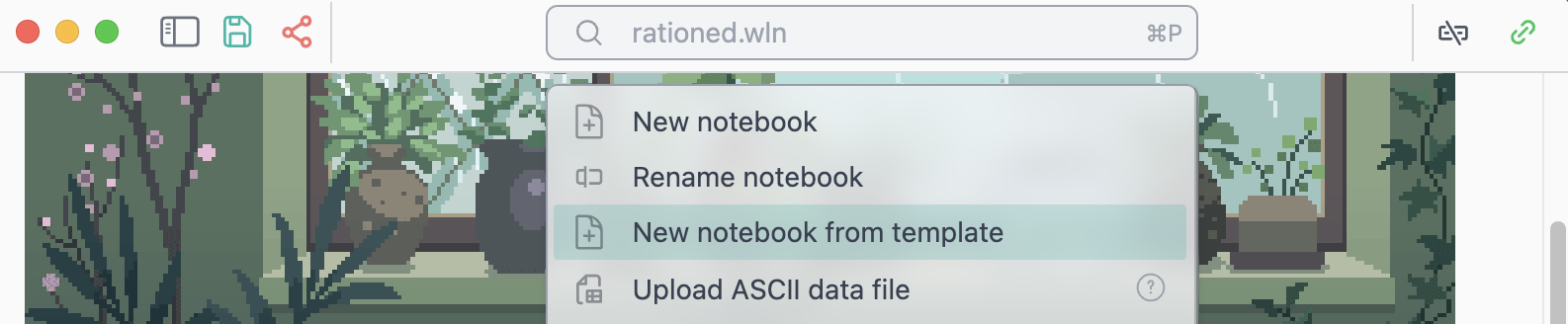
Uploading data
There are a few snippets used for uploading ASCII data or any arbitrary files to the folder of your notebook
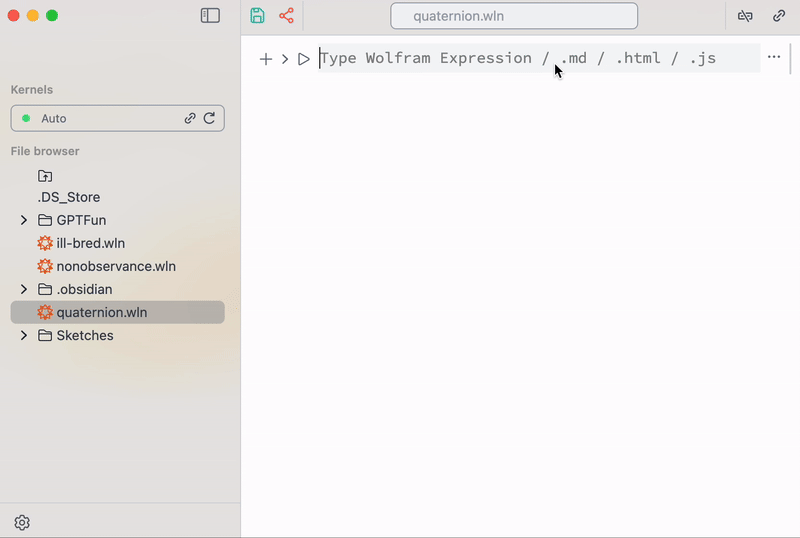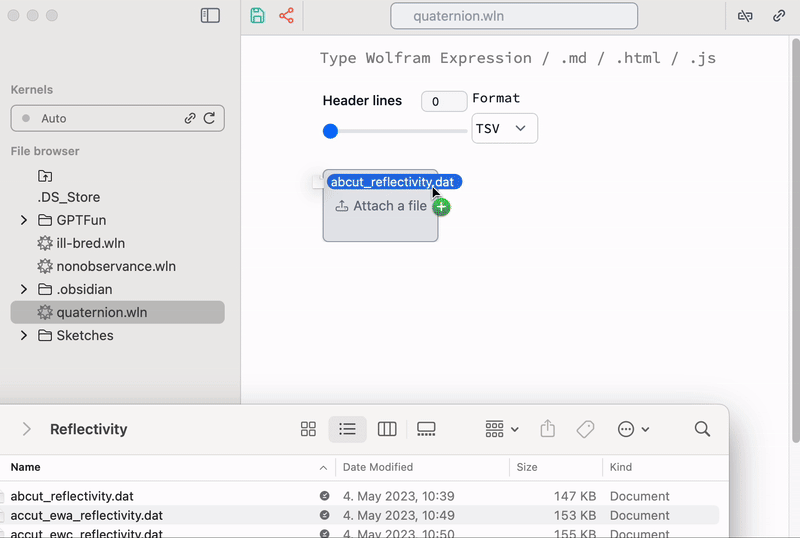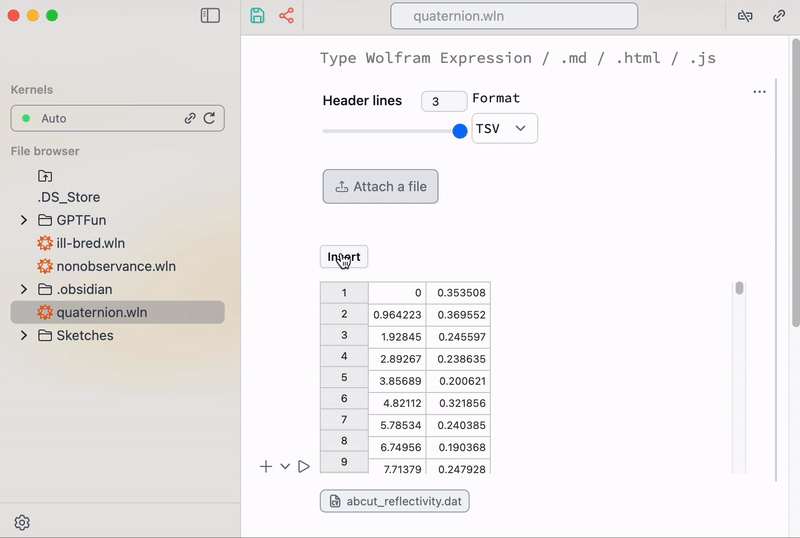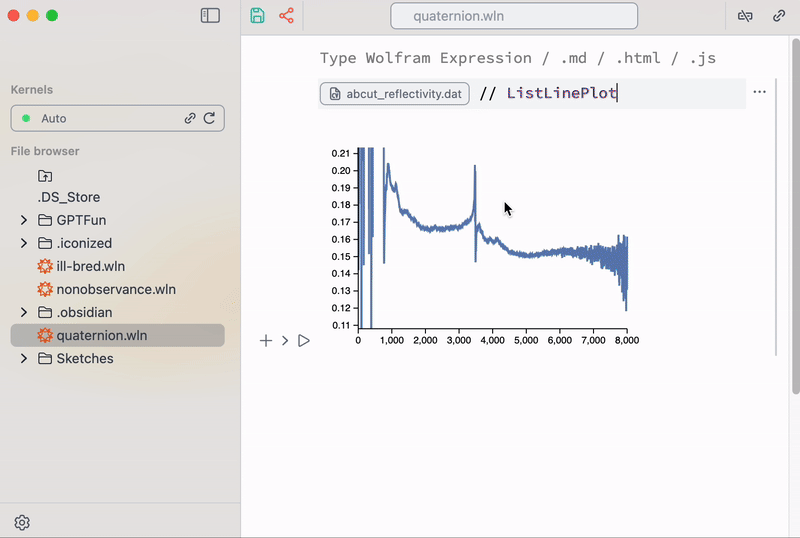
This snippet was built using regular Wolfram Language.
Special characters
A toolbar with templates for symbolic integration, series and etc is also available from the command palette
However, it is recommended to use keyboard shortcuts for
- fractions
Ctrl+/ - subscripts
Ctrl+- - power
Ctrl+6 - square roots
Ctrl+2 - greek symbols
ESC+al,ESC+be,ESC+ga,ESC+o...
Matrix helper
To make it easier for typing matrixes, one can use the following snippet
-bd2e4754fce9c93a37bf52db74ce03d4.gif)
This snippet inserts the given matrix into the cell where your last cursor was. A snippet was made using WLX cells for better customized look.
Show available options
This snippet analyses the content of your cell from the left of your cursor position and prints Options for a given symbol
-7a237c29f6d38e4c985af81031538e27.gif)
Drop a cursor in the middle of a symbol of interest. You can select and edit option values inside the picker
Not all options are supported for a standard library symbol of Wolfram Mathematica
Navigation gizmo
This feature is aimed to slightly blur the line between code and traditional GUI interface approaches for 2D/3D graphics design
-a5b564409586bc3434e3c63a91b22453.gif)
See shorts on that
It utilizes the dynamic reevaluation features of WLJS Notebook as well as powerful syntax sugar of an input editor.
- Select 2D or 3D list of coordinates
{} - Type
gizmo...in the command palette - Evaluate the cell
- Drag gizmo to the desired position and click on a check mark
It can also work in principle for most primitives
-e08e04dd44047ac3f3d601cbfc0416f8.gif)
Add an offset to a manipulated list, that a gizmo will not overlap with other graphics primitives. For example
Offload or (Hold will also work) is necessary here to prevent Wolfram Kernel from distributing Plus over each position of the list.
Or for 3D primitives as well
-5df85d0d9d86f829766b4b4aeb65b26b.gif)
Format Wolfram Language code
This is also a code formatter available
-fbeba4781669232c6a70693624b7f1b5.gif)
It acts on a selected text or on the entire cell if nothing is selected
Text formatting
This snippet provides some basic tool for styling Wolfram expression, as well as text on slides, HTML and Markdown (it tries to guess the cell type and use a suitable method for each cell type)
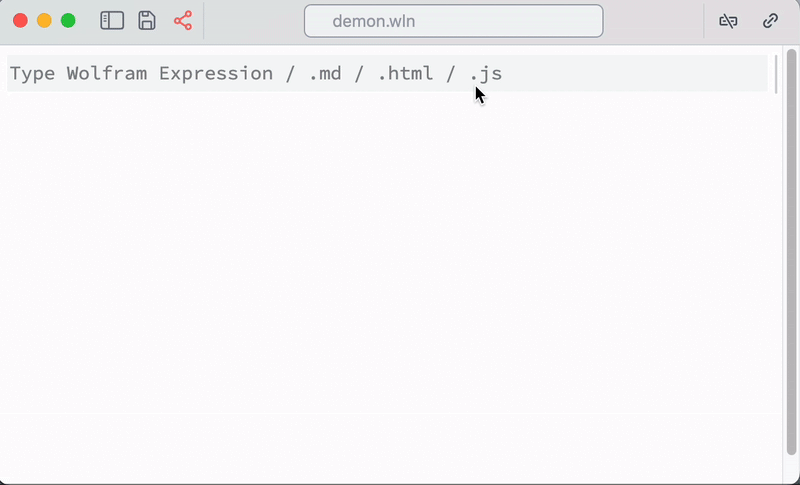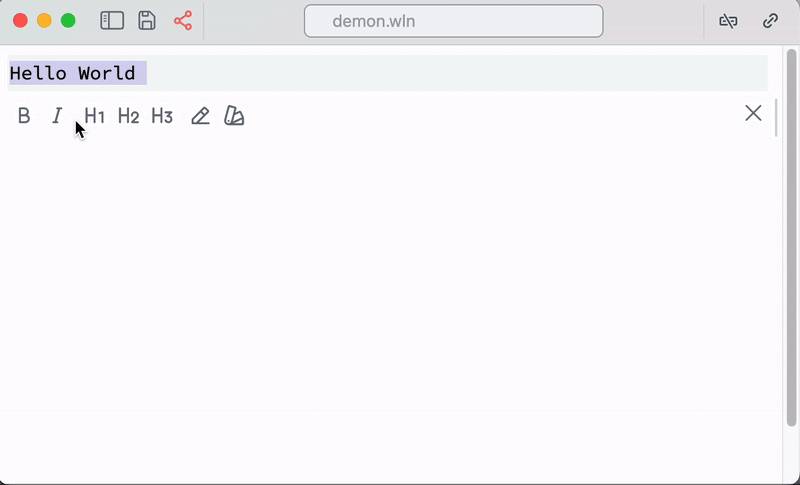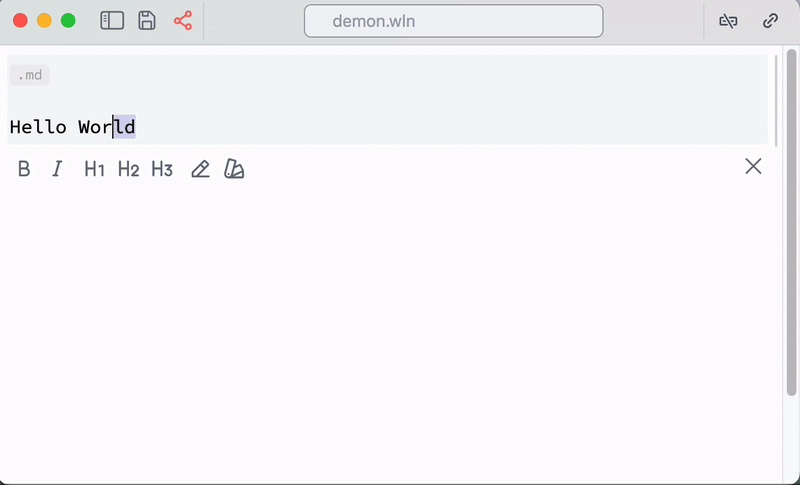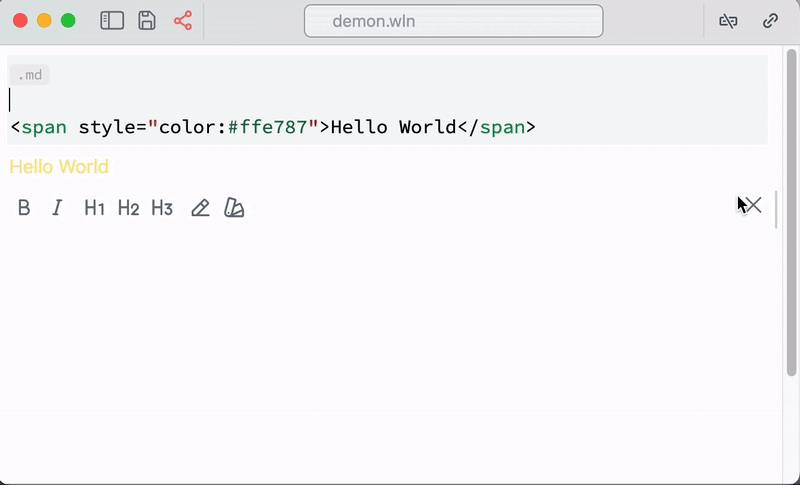
This feature is quite primitive and still in development
Take a picture
It uses your active web camera pipes a picture to Wolfram Kernel as Image object
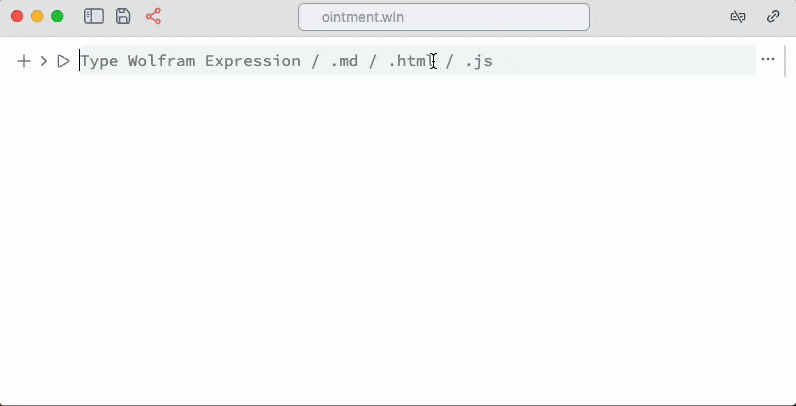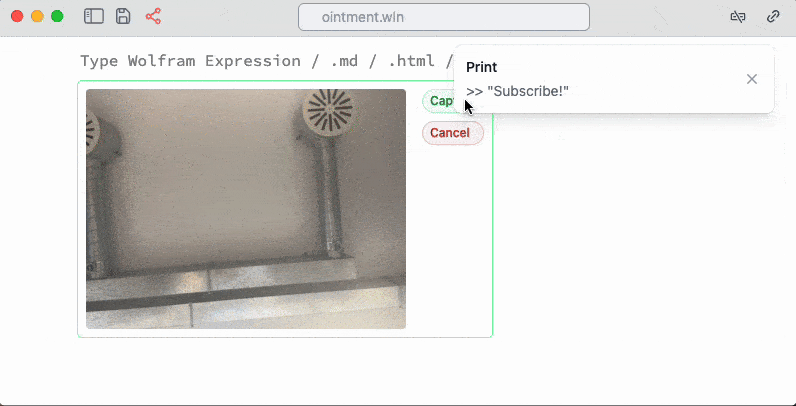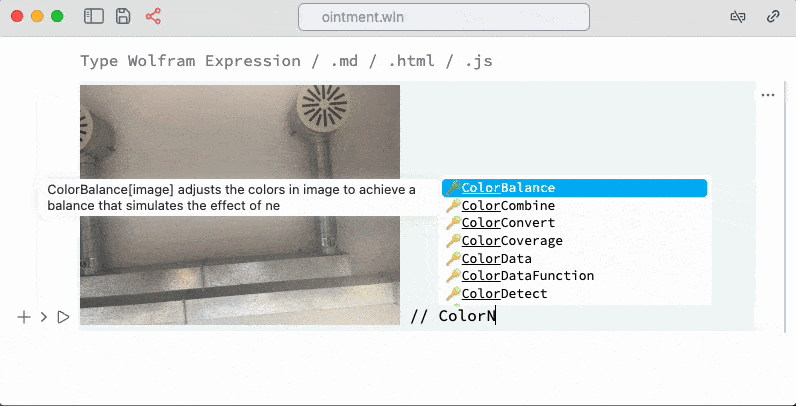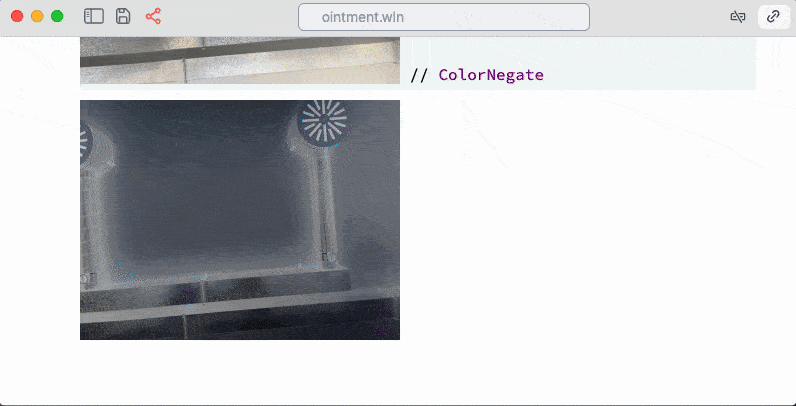
Install Wolfram Packages from Github
If you past a url to a Github repository into command palette, which contains PacletInfo.wl file in the root directory
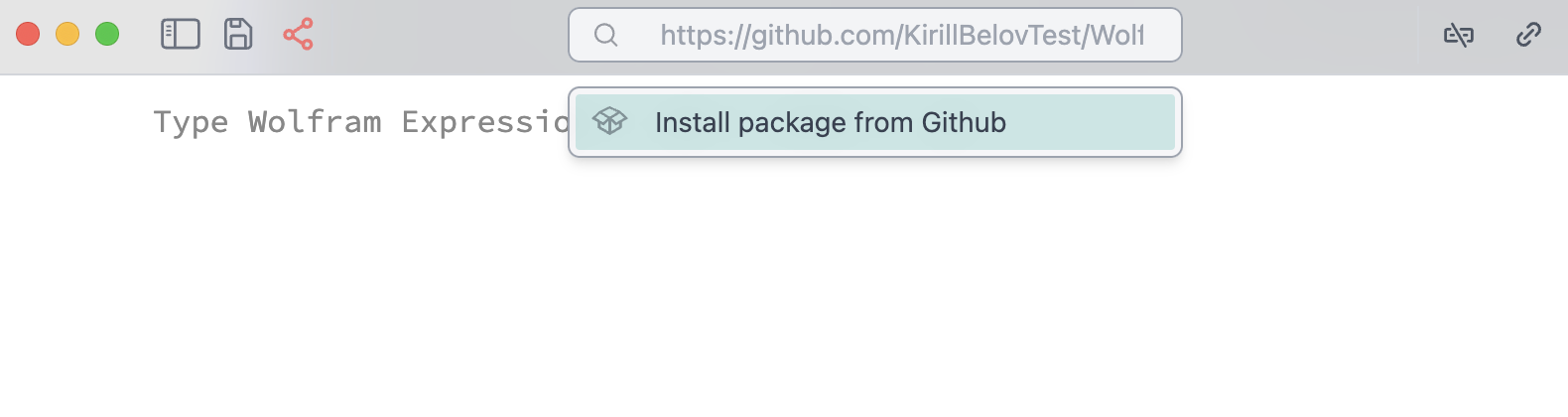
it will automatically install it locally in the folder of the current notebook.
Terminal
A direct access to the master or any evaluation kernel
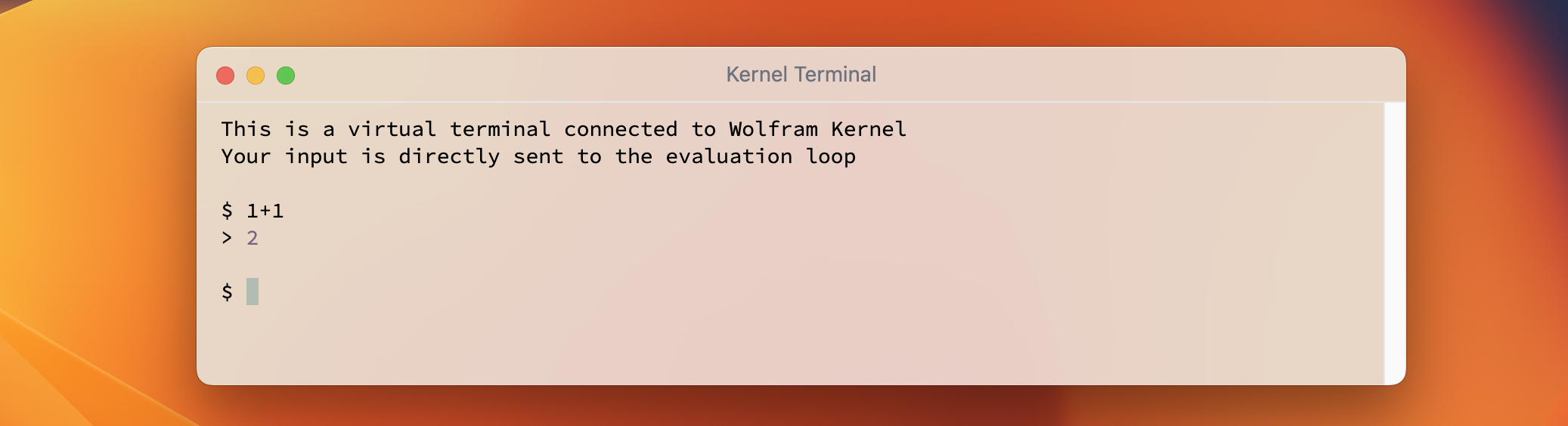
The output is formatted and colored. The default form is InputForm
Debugger
There is a build-in debugger, which allows to watch symbols, pause and inspect execution of the cells
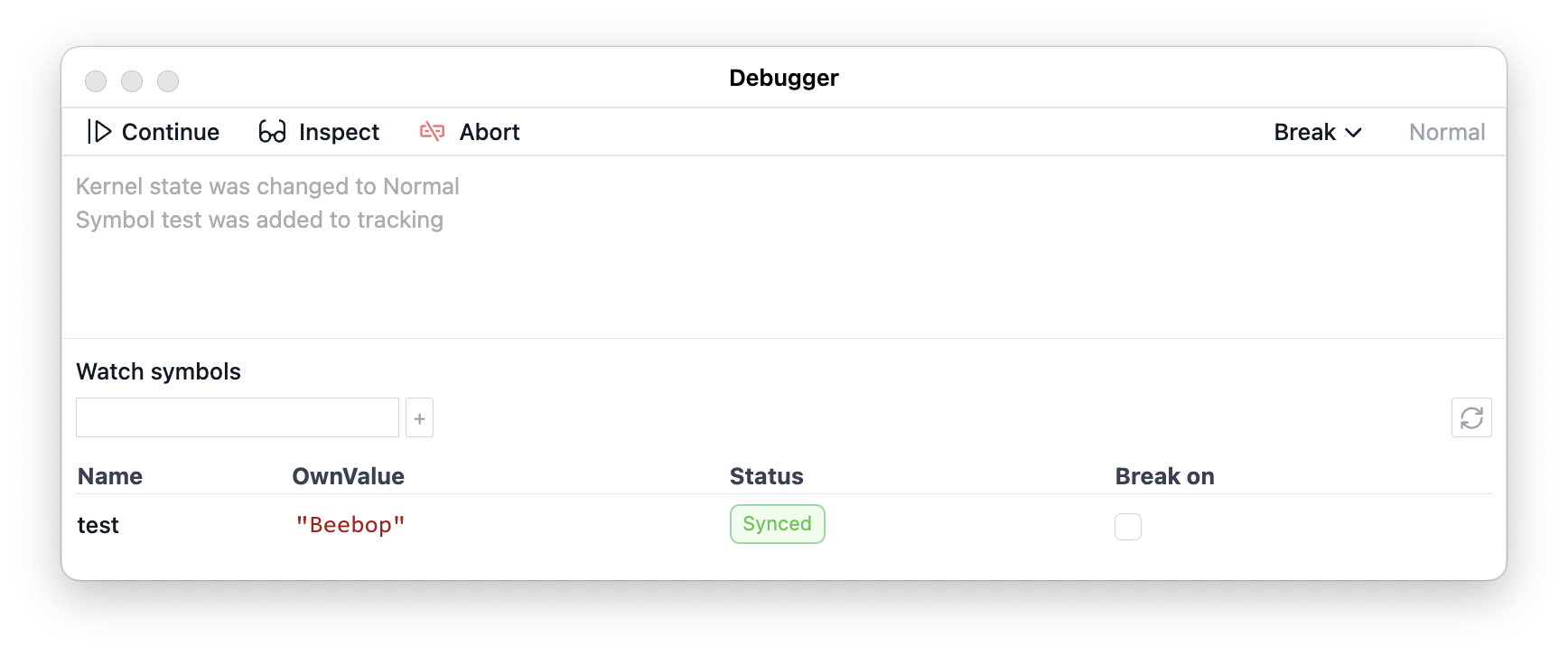 See Debugger more.
See Debugger more.
AI Assistant
If nothing is selected, the given text in the command palette is sent to ChatGPT that has an access to your notebook
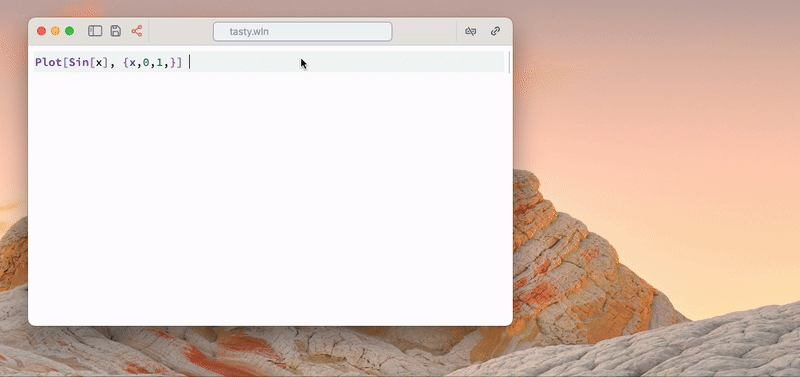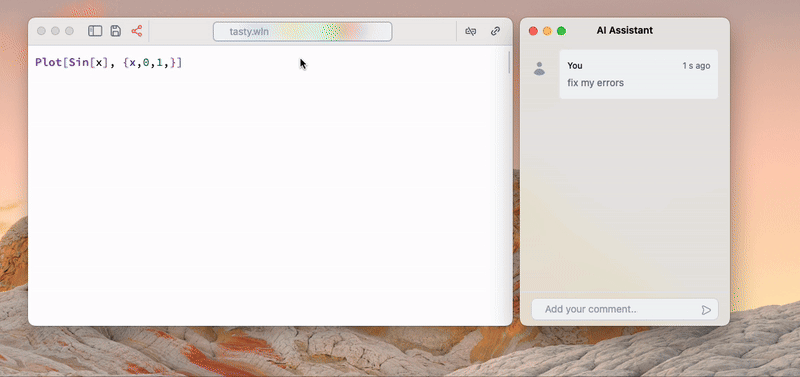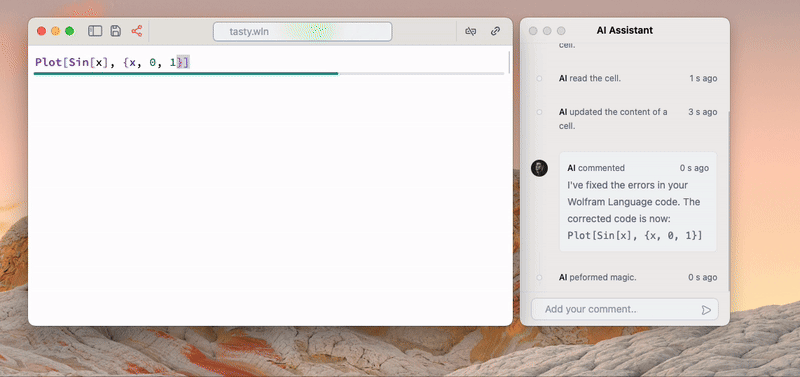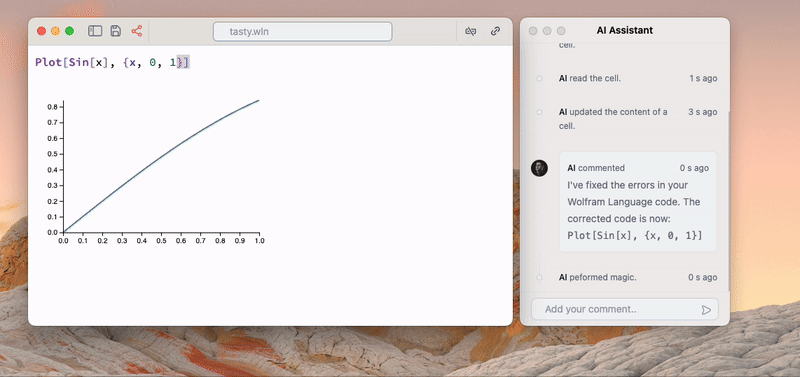
See more detailed guide on our assistant.
It will ask you for a OpenAI API Key. You need to issue it first on the official openAI website
We use the concept of a library or Knowledge on demand, which means that all additional information about notebook cell types and etc is accessible on demand, and it won’t use up your tokens if your request doesn’t match the topic.
In general AI can do the following
- create, remove, evaluate, edit cells in any language
- read notebook structure
- see and edit your focused cell you dropped a cursor on
- see and edit your selection in any editor area
- check and read the knowledge library
googleuse WolframAlpha to fetch data from the internet
Shorts