REST
API is provided by a core extension wljs-api. All communication is done via HTTP POST request in JSON format. In a nutshell it allows to
- create transactions to evaluate Wolfram, WLX, any other support languages (see Cell Types) code and get back the result
- control evaluation kernels
- fetch Frontend Objects used for 3D, 2D graphics
- fetch extensions, assets
In principle public REST API is rich enough to write your own small notebook interface with full support of all available cell types, 3D graphics, sound and etc. However, this is a natural limitation - dynamics or event-based expressions such as InputRange or Manipulate are not going to work.
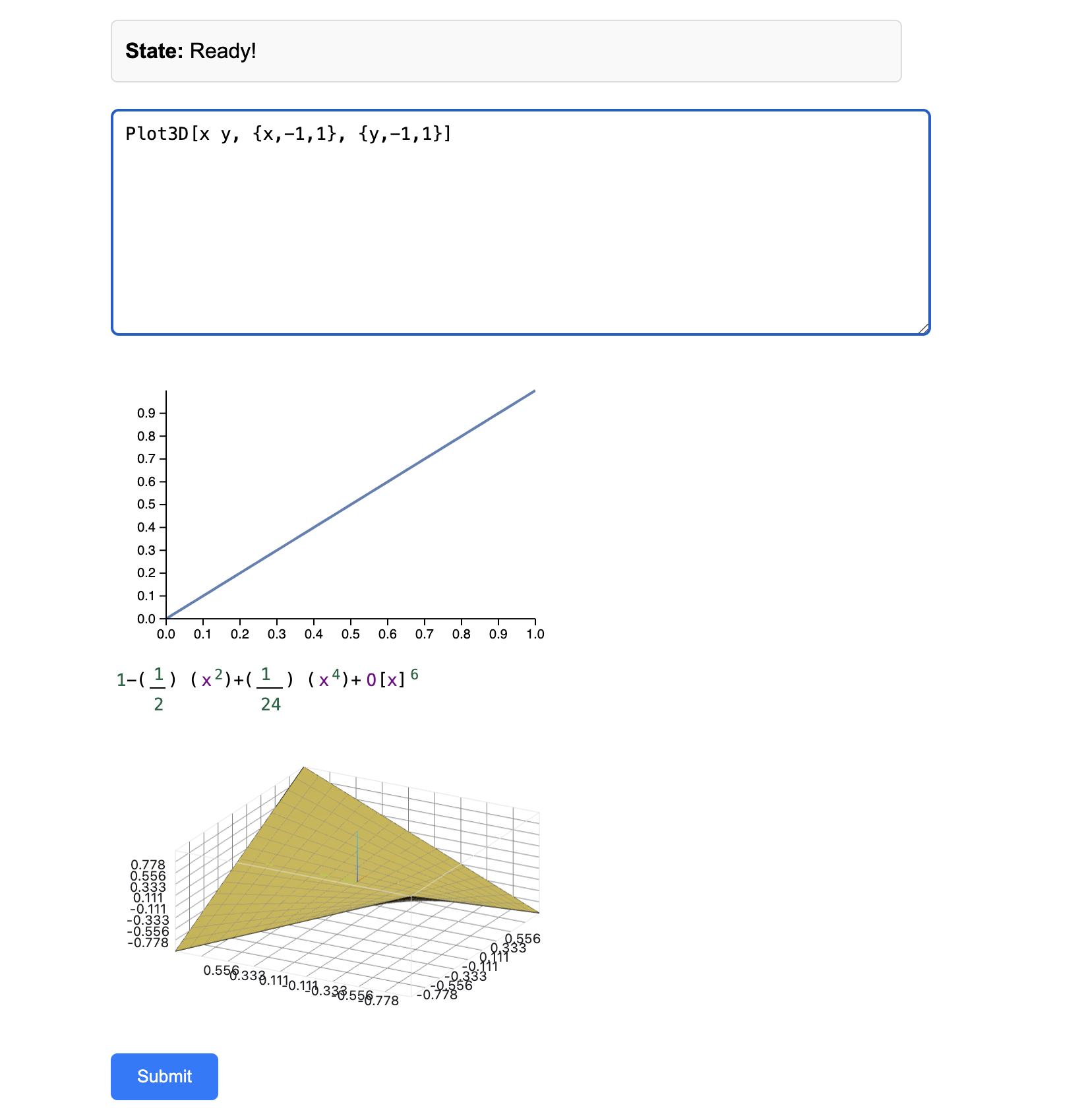
A basic example of a single HTML file REPL interface made using this API See at the bottom
WLJS System due to its architecture requires to have a few objects / interfaces to be exposed to the global window scope. We are not using ESM-like modules and bundling on purpose.
WLJS packages includes both Wolfram Language and Javascript code, therefore for the simplicity we inject JS modules to the runtime using IIFE approach or via global scope objects.
Steps to set up REPL
To make a sort of interactive evaluation environment using REST API and WLJS Notebook runtime you need to
- Wait for link to be ready
- Fetch extensions and their Javascript / CSS assets (probably cache it)
- Embed extension assets to your page (run them)
- Wait for evaluation Kernel to be ready (or create one)
- Make transaction for evaluation
- Wait for the result
- Print the result
- (Optional) fetch required frontend objects
Routes
You can see all available routes by fetching (GET or POST) via HTTP the address
http://id:port/api/
For example
fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/', {
method:'POST'
}).then((res) => {
res.json().then((r) => {
console.log(r);
});
})
will return
[ '/api/kernels/', '/api/transactions/', '/api/frontendobjects/', '/api/extensions/', '/api/ready/' ]
Link check
Route: /api/ready/
This route returns a single JSON object
{
ReadyQ: <state>
}
If <state> is true, system is ready to work.
Example
To check connection you might use something like this
// Utility function for delay
const delay = (ms) => new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
const checkConnection = async () => {
try {
const res = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/ready/', { method: 'POST' });
console.warn(res);
const r = await res.json();
if (!r.ReadyQ) {
await delay(300);
await checkConnection();
}
} catch (err) {
await delay(300);
await checkConnection();
}
};
Extensions and assets
We call assets all 2d, 3d, sound libraries, view-components of cells and other support modules used rendering the output of Wolfram Language.
List of extensions
Route: /api/extensions/list/
lists all extensions and their versions enabled on the system and required for evaluation
[
{name: <name1>, version: <version1>},
...
]
Javascript assets
Route: /api/extensions/get/minjs/
Body : [<name1>, <name2>, ...]
it will request all Javascript assets in minified CJS format and return them in the same order as array of url-encoded strings
[
<urlEncodedText>,
...
]
Use type="module" for each script provided in the response.
For example, one can request them first using List and embed to head of the document
// Fetch extensions list
const listRes = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/list/', { method: 'POST' });
const listData = await listRes.json();
console.log(listData);
const exts = listData.map((e) => e.name);
console.log(exts);
// Fetch minified JS
const jsRes = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/get/minjs/', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(exts),
});
const jsData = await jsRes.json();
jsData.forEach((src) => {
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.type = 'module'; //since it is CJS
script.innerHTML = decodeURIComponent(src);
document.head.appendChild(script);
});
CSS assets
Route: /api/extensions/get/styles/
Body : [<name1>, <name2>, ...]
it will request all CSS assets and return them in the same order as array of url-encoded strings
[
<urlEncodedText>,
...
]
Example
A minimal example in Javascript to fetch all assets and embed them
const fetchExtensions = async () => {
try {
// Fetch extensions list
const listRes = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/list/', { method: 'POST' });
const listData = await listRes.json();
console.log(listData);
const exts = listData.map((e) => e.name);
console.log(exts);
// Fetch minified JS
const jsRes = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/get/minjs/', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(exts),
});
const jsData = await jsRes.json();
jsData.forEach((src) => {
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.type = "module";
script.innerHTML = decodeURIComponent(src);
document.head.appendChild(script);
});
// Fetch styles
const styleRes = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/get/styles/', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(exts),
});
const styleData = await styleRes.json();
styleData.forEach((src) => {
const style = document.createElement('style');
style.innerHTML = decodeURIComponent(src);
document.head.appendChild(style);
});
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error fetching extensions:', err);
}
};
JS Bundle
Temporary broken. Do not use
Route: /api/extensions/bundle/minjs/
requests a single JS module containing all necessary scripts
'uriEncodedString'
Example
Fetch the bundle and embed it
fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/bundle/minjs/', {
method:'POST'
}).then((res) => {
res.json().then((r) => {
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.type="module";
script.innerHTML = decodeURIComponent(r);
document.body.appendChild(script);
//after it was loaded, you can continue in setting up thing
});
})
CSS Bundle
Route: /api/extensions/bundle/styles/
Kernels management
By the default WLJS Notebook starts and initializes 1 evaluation Kernel. The default WRI license of Wolfram Engine does not allow to spawn more.
List of kernels
Route: /api/kernels/list/
returns a list of objects representing state of kernels
[
{
Hash: <hash1>,
State: <state1>,
Name: <name1>,
ReadyQ: <ready1>,
ContainerReadyQ: <cready1>
},
...
]
where Hash is used as uid of a given Kernel used later in evaluation. State field or ReadyQ represents the status of the Kernel itself, while ContainerReadyQ represents the state of evaluator running inside Kernel standing for different cell types / languages.
For example
ReadyQ: true,
ContainerReadyQ: false
ReadyQ: true,
ContainerReadyQ: true
Read state of Kernel
Route: /api/kernels/get/
Body : {Hash: <hash>}
returns the state of a given kernel
{
Hash: <hash>,
State: <state>,
Name: <name>,
ReadyQ: <ready>,
ContainerReadyQ: <cready>
}
Restart Kernel
Route: /api/kernels/restart/
Body : {Hash: <hash>}
restarts a given kernel. You would need to reinitialize it afterwards
Initialize Kernel
Route: /api/kernels/init/
Body : {Hash: <hash>}
initializes a given kernel
Deinitialize Kernel
Route: /api/kernels/deinit/
Body : {Hash: <hash>}
deinitializes a given kernel
Abort evaluation
Route: /api/kernels/abort/
Body : {Hash: <hash>}
aborts running evaluation (if there is one)
Example
A minimal example to find ready kernels
const delay = (ms) => new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
const findKernel = async () => {
const res = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/kernels/list/', {
method:'POST'
});
const body = await res.json();
const valid = body.filter((el) => el.ContainerReadyQ);
if (valid.length == 0) {
await delay(300);
return await findKernel();
}
return valid[0].Hash;
}
Transactions
The evaluation is performed using a so-called transaction. This refers to a type of evaluation query used by cells in the WLJS Notebook. Each created transaction is immediately submitted to the designated Kernel for evaluation. Once the evaluation is complete, its state field changes to Idle, and the user can retrieve the result.
List transactions
Route: /api/transactions/list/
returns a list in the form
[
{
Hash: <hash>,
State: <state>
},
...
]
where Hash is used as uid to refer to individual transaction object.
Create transaction
Route: /api/transactions/create/
Body: {Kernel: <kernelHash>, Data: <data>}
where <Data> is an input string with your code to be evaluated. Since it uses the same pipeline of evaluation as notebook cells, you can provide not only Wolfram Language code, but any other supported language
{
Kernel: 'uid of a kernel',
Data: 'Plot[x, {x,0,1}]'
}
{
Kernel: 'uid of a kernel',
Data: '.wlx\n\n <div><Now/></div>'
}
The response will contain uid (or Hash) of created transaction
<Hash>
where <Hash> is a plain string.
Get transaction
Route: /api/transactions/get/
Body : {Hash: <hash>}
requests information about provided transaction. In the case if transaction is still under evaluation
{
Hash: <hash>,
State: 'Evaluation'
}
when evaluation has finished
{
Hash: <hash>,
State: 'Idle',
Result: <result>
}
where <result> is an object
{
Data: <dataString>,
Display: <display> || "codemirror"
}
Here the output string is stored in Data field, while Display defines a key-values of a view-component to render the output content.
If Display is not provided, it is assumed, that it is "codemirror" - a default view component available in WLJS (see later).
Delete transaction
Route: /api/transactions/delete/
Body : {Hash: <hash>}
removes a transaction from memory.
Example
A minimal example to evaluate something might look like
const delay = (ms) => new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
const getResult = async (kernel, transaction) => {
await delay(300);
let result = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/transactions/get/', {
method:'POST',
body:JSON.stringify({
'Hash': transaction
})
});
result = await result.json();
console.log(result);
if (!(result.State == 'Idle')) result = await getResult(kernel, transaction);
return result.Result;
}
const evaluate = async (resultsDiv, kernel, text) => {
const trimmed = text.trim();
if (trimmed.length == 0) return;
let transaction = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/transactions/create/', {
method:'POST',
body:JSON.stringify({
'Kernel': kernel,
'Data': trimmed
})
});
transaction = await transaction.json();
const results = await getResult(kernel, transaction);
console.warn(results);
results.forEach((data) => {
const display = data.Display || 'codemirror';
const parentelement = document.createElement('div');
resultsDiv.appendChild(parentelement);
const origin = {
element: parentelement
};
const cell = new window.SupportedCells[display].view(origin, data.Data);
//to remove use
//cell.dispose()
})
})
where window.SupportedCells will automatically be added to the global scope of your app if you do Extensions and assets.
Frontend Objects
Frontend Objects are used to compress large expressions from the output / input cells into references to prevent code editors from parsing them. It does not alter the original expression, but only stores it separately in JSON format.
For example if you evaluate Plot[x, {x,0,1}] as a result you will get from the transaction something like this
{
Hash: <...>
Data: "(*VB[*)(FrontEndRef[\"770b6389-c881-426a-94c4-01e2abc608ee\"])(*,*)(*1:eJxTTMoPSmNkYGAoZgESHvk5KRCeEJBwK8rPK3HNS3GtSE0uLUlMykkNVgEKm5sbJJkZW1jqJltYGOqaGJkl6lqaJJvoGhimGiUmJZsZWKSmAgB0eRVI*)(*]VB*)"
}
where "770b6389-c881-426a-94c4-01e2abc608ee" encoded in Base64-like code inside comments refers a JSON object, which contains Wolfram Language Graphics[{Line[...], ...}, ...].
If you create a cell using one of window.SupportedCells view-components like in the example above it will use a general (for WLJS) interface to fetch missing frontend objects (in a case if it contains ones) and render to the provided DOM.
Frontend objects interface
The management of those object is done internally, however, get method has to be defined explicitly
This is a global object exposed by WLJS
window.ObjectStorage.prototype.get = function () {
if (this.cached) return this.cache;
const self = this;
const promise = new Deferred();
getObject(self.uid).then((result) => {
self.cache = result;
promise.resolve(self.cache);
}, (rejected) => {
console.warn('Rejected! Not found');
promise.reject();
})
return promise.promise;
}
where getObject is a function, which gets the requested object using our API (see the implementation later).
Get object
Route: /api/frontendobjects/get/
Body : {Kernel: <kernelHash>, UId: <uid>}
Objects are stored on Kernels and need to be requested. The first API request usually requests frontend object from Kernel with a corresponding response
{
Resolved: <state>
}
You will need to pool using this method until <state> becomes true, then
{
Resolved: true,
Data: <data>
}
where <data> is URL-encoded JSON string, which contains the desired object.
Example
Following the previous example, one can implement getObject in the following way assuming that you store Kernel hash in a global variable targetKernel
const targetKernel = '...';
const getObject = async (uid) => {
let r = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/frontendobjects/get/', {
method:'POST',
body:JSON.stringify({
'UId': uid,
"Kernel": targetKernel
})
});
r = await r.json();
if (r.Resolved == true) {
return JSON.parse(r.Data);
}
await delay(300);
return await getObject(kernel, uid)
}
Minimal example of REPL
Using a single HTML file and a bunch of Javascript code one can make a working REPL interface using our API
Details
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Textarea Template</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
margin: 20px;
line-height: 1.6;
}
.container {
max-width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.state {
margin-bottom: 20px;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
textarea {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
resize: vertical;
}
button {
display: block;
margin: 10px 0;
padding: 10px 20px;
background-color: #007bff;
color: #fff;
border: none;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #0056b3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="state">
<strong>State:</strong> <span id="stateField">Waiting for wljs connection</span>
</div>
<textarea id="code_area" placeholder="Type your text here...">Plot[x, {x,0,1}]</textarea>
<div id="resultsDiv"></div>
<button id="submit_button" type="button">Submit</button>
</div>
<script type="module">
const stateField = document.getElementById("stateField");
const submitButton = document.getElementById("submit_button");
const codeArea = document.getElementById("code_area");
const resultsDiv = document.getElementById('resultsDiv')
// Utility function for delay
const delay = (ms) => new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
const checkConnection = async () => {
try {
const res = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/ready/', { method: 'POST' });
console.warn(res);
const r = await res.json();
if (!r.ReadyQ) {
await delay(300);
await checkConnection();
}
} catch (err) {
await delay(300);
await checkConnection();
}
};
const fetchExtensions = async () => {
try {
stateField.innerText = 'Fetching extensions...';
// Fetch extensions list
const listRes = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/list/', { method: 'POST' });
const listData = await listRes.json();
console.log(listData);
const exts = listData.map((e) => e.name);
console.log(exts);
// Fetch minified JS
const jsRes = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/get/minjs/', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(exts),
});
const jsData = await jsRes.json();
jsData.forEach((src) => {
const script = document.createElement('script');
script.type = "module";
script.innerHTML = decodeURIComponent(src);
document.head.appendChild(script);
});
// Fetch styles
const styleRes = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/extensions/get/styles/', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(exts),
});
const styleData = await styleRes.json();
styleData.forEach((src) => {
const style = document.createElement('style');
style.innerHTML = decodeURIComponent(src);
document.head.appendChild(style);
});
} catch (err) {
console.error('Error fetching extensions:', err);
}
};
let targetKernel;
const findKernel = async () => {
const res = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/kernels/list/', {
method:'POST'
});
const body = await res.json();
const valid = body.filter((el) => el.ContainerReadyQ);
if (valid.length == 0) {
await delay(300);
return await findKernel();
}
return valid[0].Hash;
}
const getResult = async (kernel, transaction) => {
await delay(300);
let result = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/transactions/get/', {
method:'POST',
body:JSON.stringify({
'Hash': transaction
})
});
result = await result.json();
console.log(result);
if (!(result.State == 'Idle')) result = await getResult(kernel, transaction);
return result.Result;
}
const setUpServerAPI = () => {
const getObject = async (kernel, uid) => {
let r = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/frontendobjects/get/', {
method:'POST',
body:JSON.stringify({
'UId': uid,
"Kernel": kernel
})
});
r = await r.json();
if (r.Resolved == true) {
return JSON.parse(r.Data);
}
await delay(300);
return await getObject(kernel, uid)
}
//implemetation of get method depends on execution env
window.ObjectStorage.prototype.get = function () {
if (this.cached) return this.cache;
const self = this;
const promise = new Deferred();
getObject(targetKernel, self.uid).then((result) => {
self.cache = result;
promise.resolve(self.cache);
}, (rejected) => {
console.warn('Rejected! Not found');
promise.reject();
})
return promise.promise;
}
}
var initializationComplete = async () => {
setUpServerAPI();
console.warn('Initialization complete!');
stateField.innerText = 'Connecting to Kernel';
const kernel = await findKernel();
targetKernel = kernel;
console.log('Obtained Kernel '+kernel);
stateField.innerText = 'Ready!';
submitButton.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const trimmed = codeArea.value.trim();
if (trimmed.length == 0) return;
let transaction = await fetch('http://127.0.0.1:20560/api/transactions/create/', {
method:'POST',
body:JSON.stringify({
'Kernel': kernel,
'Data': trimmed
})
});
transaction = await transaction.json();
stateField.innerText = 'Evaluation...';
const results = await getResult(kernel, transaction);
console.warn(results);
stateField.innerText = 'Ready!';
results.forEach((data) => {
const display = data.Display || 'codemirror';
const parentelement = document.createElement('div');
resultsDiv.appendChild(parentelement);
const origin = {
element: parentelement
};
const cell = new window.SupportedCells[display].view(origin, data.Data);
//to remove use
//cell.dispose()
})
})
}
(async () => {
await delay(300);
await checkConnection();
await fetchExtensions();
await initializationComplete();
})();
</script>
</body>
</html>